PrestaShop comes multilingual out of the box. This tutorial explains how to localize and translate your PrestaShop E-commerce into different languages: product catalog, categories, pages, theme, modules, etc.
INDEX
3. Translator profile in PrestaShop
4. Translation modules in PrestaShop
Introduction
PrestaShop is multilanguage by default. You can make a multilingual store easily. PrestaShop core is already translated into more than 65 languages. Translations have been made by the PrestaShop community through CrowdIn (collaborative translation platform).
Note that PrestaShop core translations refer to common text strings that appear in front and back office, message error, PDF files and e-mail templates. But if you want to build a fully translated and localized PrestaShop store , you will have to translate all contents, using PrestaShop editor. Two types of content must be translated:
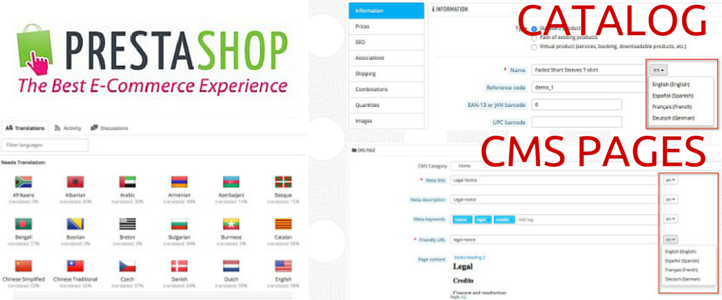
- Product catalog: title, description, attributes, friendly URLs, SEO data, etc.
- CMS pages: “About us”, “Disclaimer”, “Privacy policy”, etc.
Previous recommendations:
- Using machine translation is the cheapest option, but not the most advisable since translations often don’t make sense and Google could consider them as spam.
- Performs translations by professional translators (owned or hired). If you do not have time or budget resources, better not make a multilingual E-commerce shop. There is nothing wrong with translating some of most important pages (e.g. ‘About us’), but it’s unprofessional to have only half your products translated
- This tutorial refers to the translation of a single PrestaShop store into other languages with the same products and using subdirectories (https://myshop.com/es, for the Spanish version, https://myshop.com/de, for the German version, etc.)
- There is another option to create a multilingual shop using multistore, managing several stores, each with its own language and currency, but with a single administration panel. This option can be useful when different products are sold in each market and if you want to use country code top-level domain (https://myshop.es for the Spanish version, https://myshop.fr, for the French version, etc.)
1. Install language package
In PrestaShop, it is very easy to install a language pack that include not only translations, but currencies, taxes, units, etc. Navigate to LOCALIZATION > Localization, choose a country and import a language pack. On the same page you can also set the default language, country and currency.
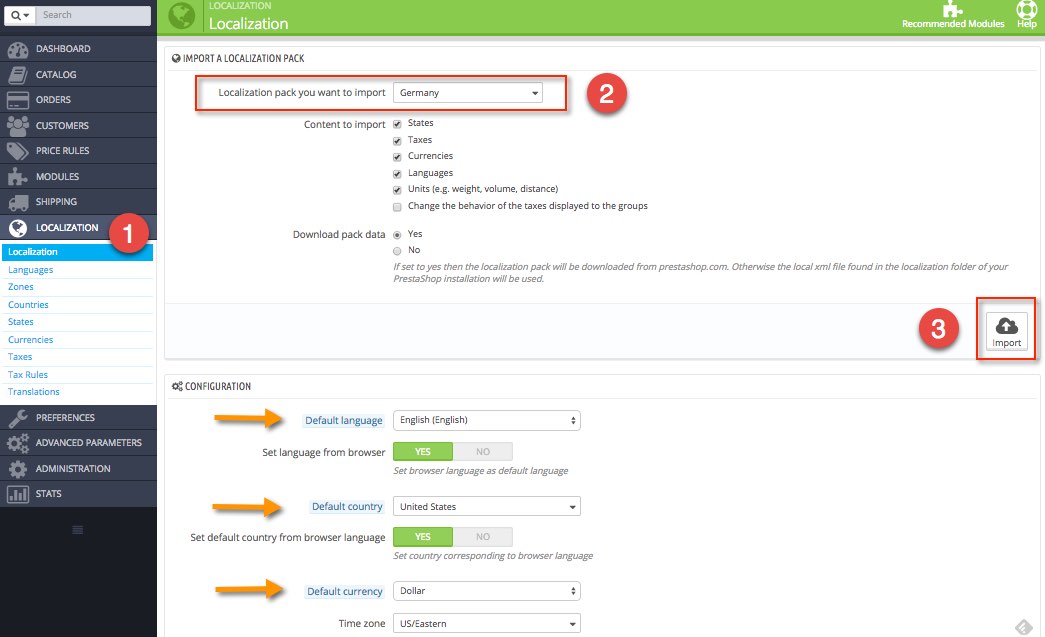
Once language pack is installed, go to LOCALIZATION > Translations, and you can view and edit translations.
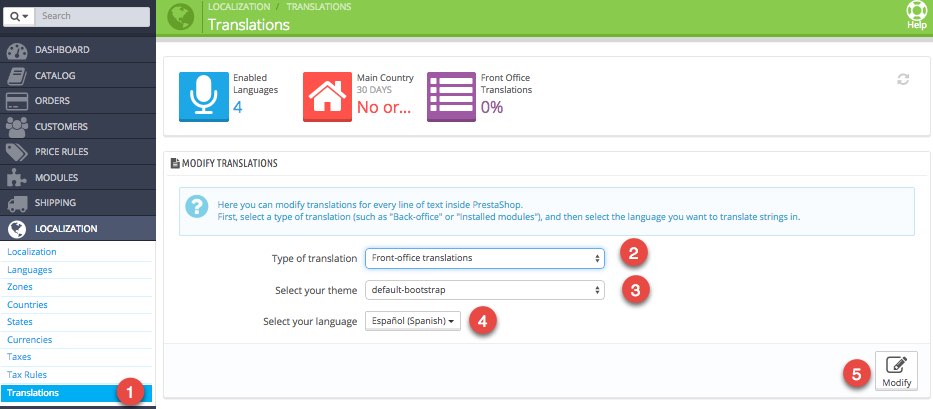
There are different types of translations:
- Front Office. Translations are visible in store for customers. For example, Search = Buscar, i.e. the text that appears in PrestaShop search engine.
- Back Office. Translations of admin panel
- Error message. Error messages translations. For example: The Zip/Postal code you’ve entered is invalid. It must follow this format: %s = Código postal inválido. Debe ser escrito como sigue:%s. As you can see some of these expressions use special syntax (for example: %s). You must use this syntax in your translations.
- Field name. Field name translations in front and back office. For example: phone_mobile = teléfono_móvil
- Installed modules. Translations used by the installed modules.
- PDF. String text that appear in PDF files (e.g. invoices)
- Email templates. Email templates translations.
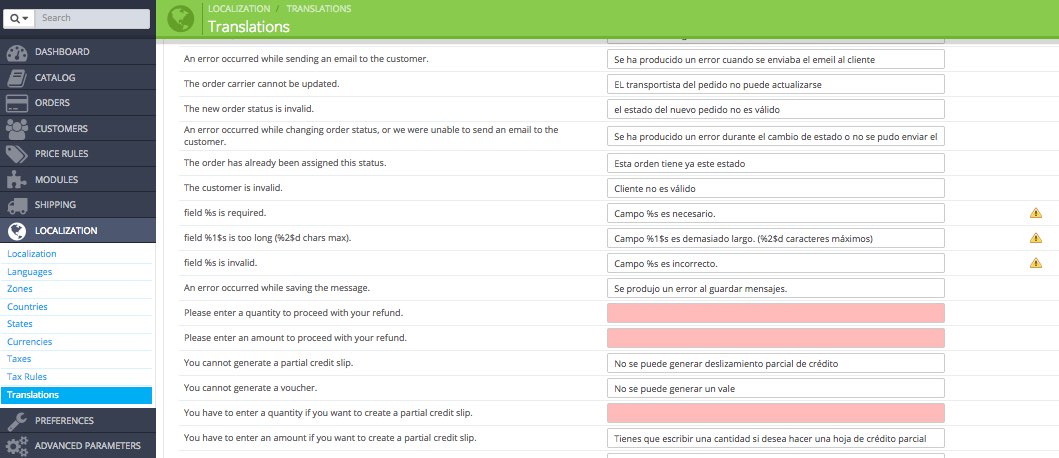
Usually it is not necessary to modify these translations, except in any of the following cases:
- Missing translations in some languages (marked in pink). Keep in mind that translations have been made by PrestaShop community.
- Maybe you installed a module or theme that doesn’t come fully translated into your language.
- You may want to customize the texts in your store: it is not the same selling luxury jewelry or skateboards for teenagers.
2. Translating contents
The most important parts that must be translated in PrestaShop are the product catalog and static pages. These contents must be translated into the PrestaShop editor. If you do not want translations to be displayed until they are completed, you can disable languages in LOCALIZATION > languages.
2.1. Product catalog
The translation of the product catalog is the most important part. Next to each field you will find a language code, which enables you to choose the language into which you wish to edit translations.
When you import a new language pack, PrestaShop automatically copies the texts of the default language into the other languages, so whenever you choose a language from the drop-down menu you will have to overwrite texts.
In this regard, these are the most important elements that need to be translated:
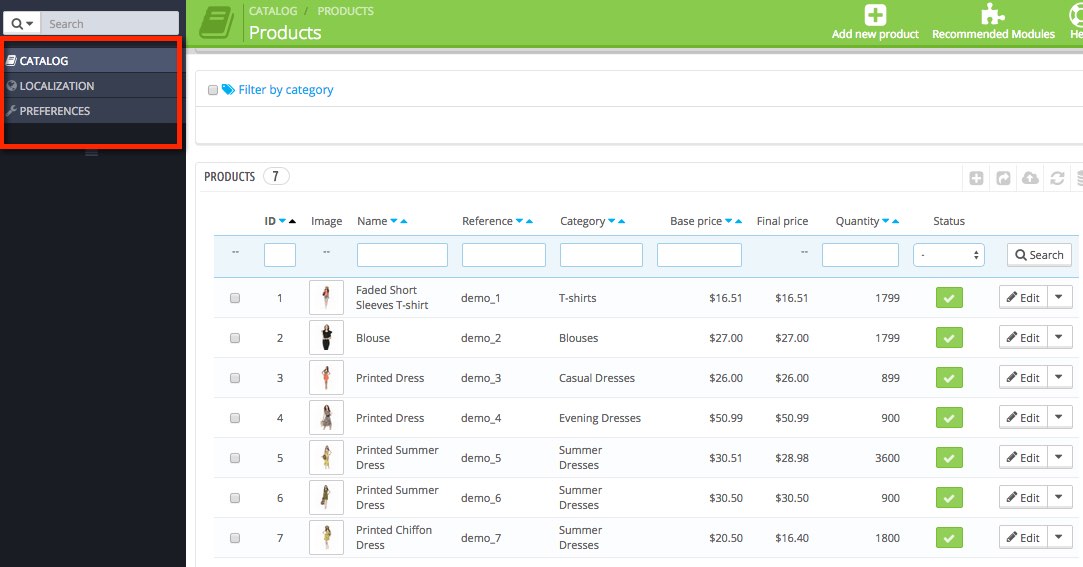
CATALOG > Products
- Information: Product name, descriptions, and tags
- SEO: Meta title, meta description, and friendly URL
- Images: Caption
- Attachments: Filename and description
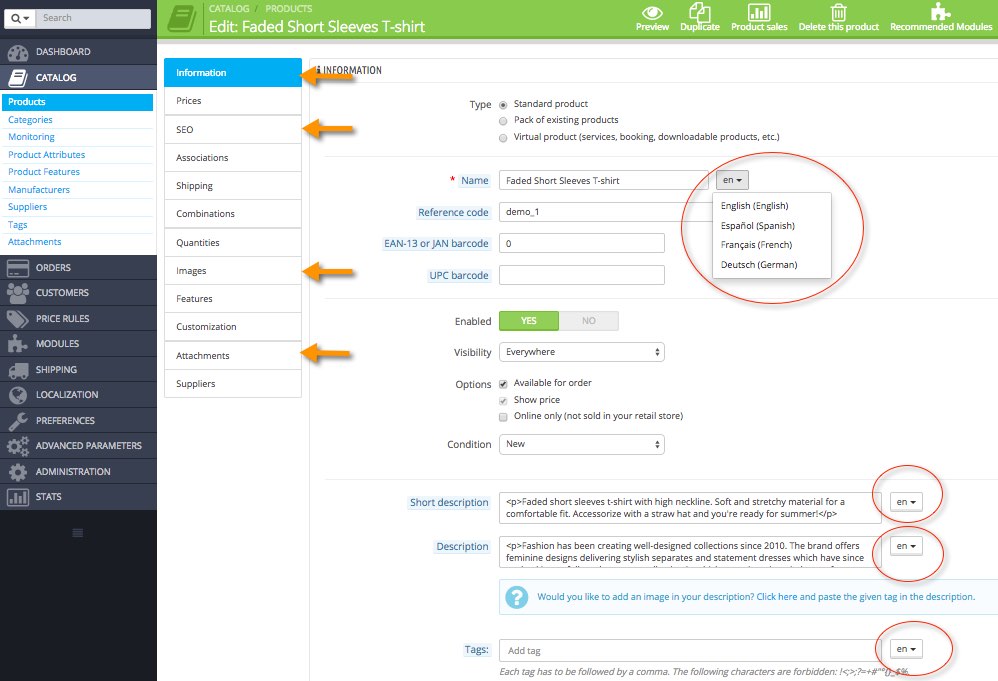
CATALOG > Categories
- Name
- Description
- Meta title
- Meta description
- Friendly URL
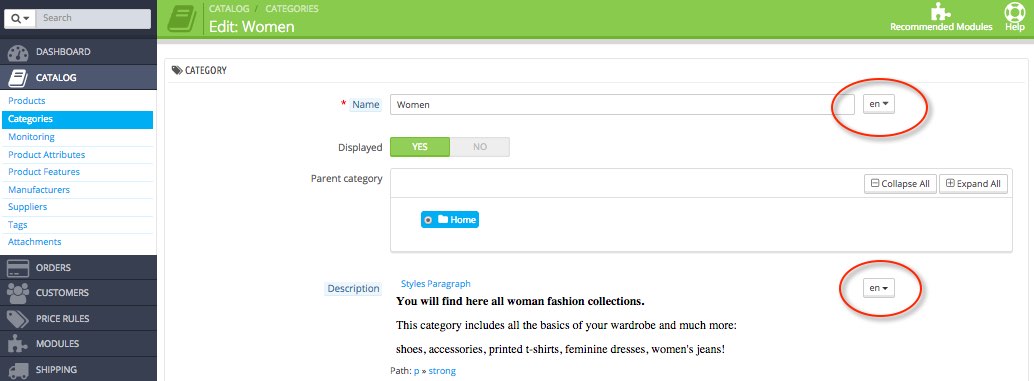
CATALOG > Product Attributes
- Name
- Public name
- URL
- Meta title
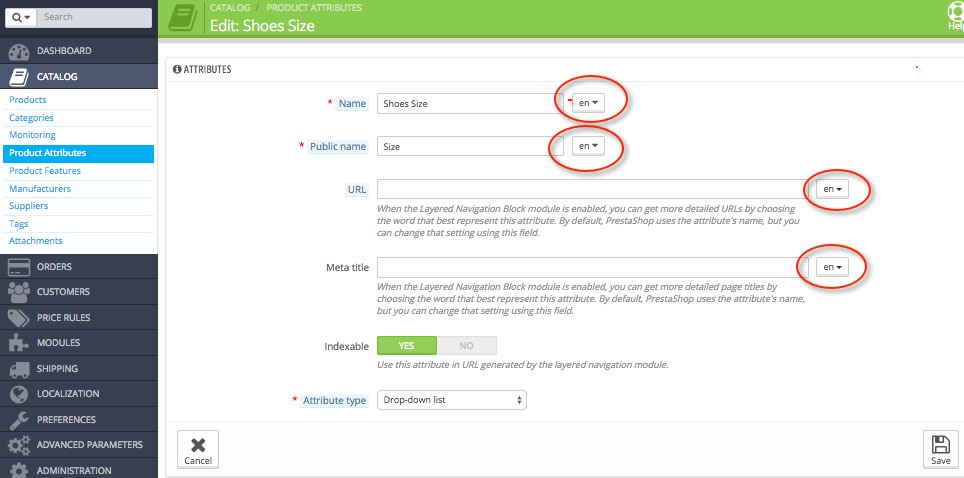
CATALOG > Product Features
- Name
- URL
- Meta title
2.2. Pages (CMS)
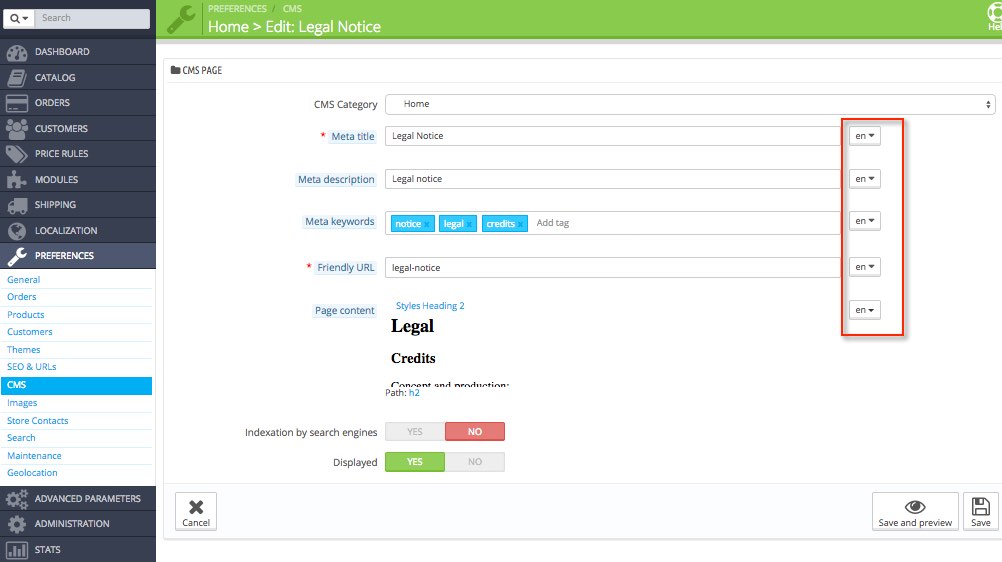
To translate pages you must navigate to PREFERENCES > CMS, and edit pages. Static pages refer to those pages that usually do not change (or change little) over time: “Legal notice”, “About us”, “Privacy policy”, etc. These are the texts that must be translated:
- Meta title
- Meta description
- Friendly URL
- Page content
Note: To translate titles in blocks you will have to go to MODULES > Modules > CMS Block, and edit names.
3. Translator profile in PrestaShop
PrestaShop allows you to create users (referred to as employees) with translator’s profile, so that it can perform translation from the administration panel. Translator will have access to the contents that need to be translated, but not to private data (customers, suppliers, sales, expenses, etc).
Adding a new translator is pretty straightforward: navigate to ADMINISTRATION > Employees > Add new employee. When it creates a profile in PrestaShop (either logistician, translator or salesman) you can choose the language from the admin panel. Each user can also change their preferred language.
The more complex part comes when setting the new profiles access rights. This is done in ADMINISTRATION > Permissions.
This is the admin panel of a translator:
If you don’t want to give access to the translator, another option is exporting contents in a CSV file to send it to the translator. In this case, the translator could use their Computer-assisted translation tool. This can be done by accessing the database using phpMyAdmin, but this requires advanced knowledge.
4. Translation modules in PrestaShop
PrestaShop official marketplace sells modules under category International & Localization:
- Machine translation. There are different modules that allow machine translation (Translate all, Google Translation, etc.). In my opinion, it is not advisable to use these modules, since in most cases translations do not make sense.
- Edit translations from the frontend (Inline Translation module). It allows you to edit and make translations from the Front Office. Personally I prefer to edit the translations from the Back Office.
- Translation modules that connect to online translation agencies. Some online translation agencies have developed specific modules to make easier the process of translation, such as TextMaster or Dixit.
I hope this article has helped you to translate your PrestaShop store into different languages
Thanks a lot for a nice topic and your explanations.
Best regards
Hello. Nice article! But you say automatic translation not usable? Better leave this decision on a store owner! For example i have in installed modules approx 2000 untranslated lines. I would go mad if i have to use that stupid presta tool. So scenario is: export all untranslated strings, through auto translator, then manually correct errors, in an user friendly editor (even excel is better than an online form that can crash, not save on click, work lost etc. i have all these seen while a few entered lines! ) and finally import all back into presta. I look in database (there are no entries, i looked into lng.php files but for modules there are no those files, even files that in master export are introduced, for example in master file is “themes/default-bootstrap/modules/cronjobs/translations/cs.php” but this files along others is nowhere in the presta directory structure. And master export is inparseable without presta code itself so this system is a mess and i have either to buy some 3rd party tool or study so much that i can write same tool myself. Very clever system! 🙁
Hello, i have a little problem with my prestashop magazine, if you want to help me to resolve this issue. I cant activate the language button on front office, i have the multi language shop but i cant change directly form front office, I must to chose direct from link example com/ro/ or com/en/. Thank you in advance!